Unleashing the Value of Surplus SILICON DIOXIDE in the Solvents Sector
SILICON DIOXIDE is an industrial-grade inorganic oxide renowned for its versatility and stability. Widely used across various industries, it plays a crucial role as a thickening, anti-caking, and rheology-modifying agent in solvent-based formulations. Companies often find themselves holding surplus SILICON DIOXIDE due to overproduction or changes in production needs. Rather than letting this valuable resource go to waste, businesses can repurpose their idle inventory, transforming stored chemicals into a significant revenue stream while maintaining high performance in their core applications.
Buy and Sell SILICON DIOXIDE - Surplus Solvent Chemical Trading Solutions
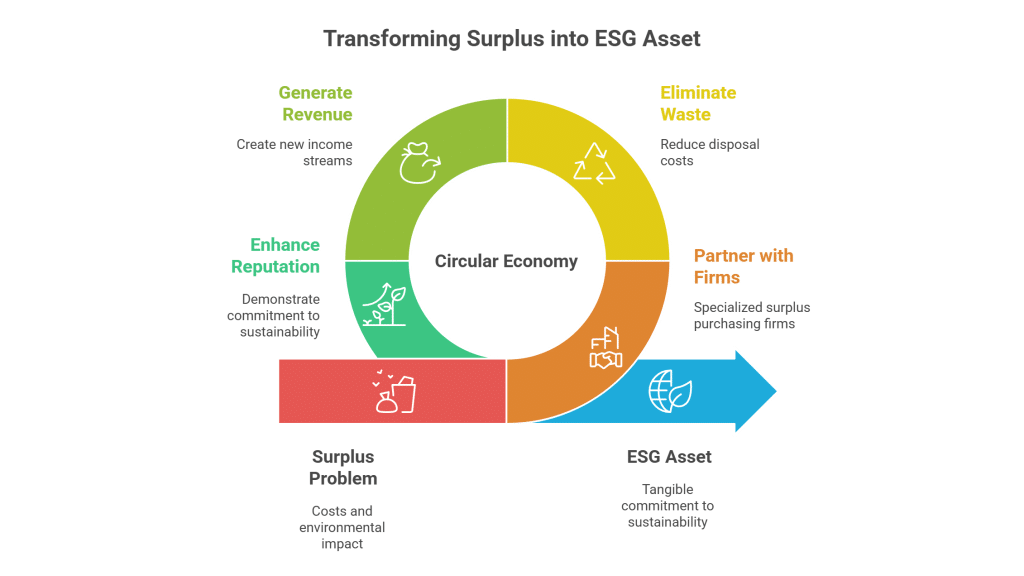
The trade of surplus chemicals, such as SILICON DIOXIDE, offers a win-win scenario for both sellers and buyers. Companies looking to offload excess inventory can recover costs, free up storage space, and reduce disposal expenses, all while boosting their sustainability credentials. On the buyer’s end, sourcing surplus SILICON DIOXIDE leads to notable cost savings, reliable access to quality materials, and an opportunity to participate in environmentally responsible practices. The proactive approach of trading surplus not only meets regulatory compliance by minimizing waste but also enhances the circular economy by ensuring chemicals are reused effectively, thereby cutting down on unnecessary disposal practices and environmental impact.
SILICON DIOXIDE and Solvents: Innovative Applications in Industrial Formulations
For buyers, purchasing surplus SILICON DIOXIDE from trusted sources ensures access to high-grade material at a reduced cost. This cost-effectiveness, combined with its reliable performance in various solvent applications, translates into significant savings and improved product quality. Buyers also gain from the availability of surplus stock, which helps in mitigating supply chain disruptions and maintaining continuous production.
Sellers benefit immensely by converting surplus SILICON DIOXIDE into an immediate revenue stream. Offloading excess stock reduces storage and handling costs while preventing the challenges associated with chemical degradation over time. Additionally, selling surplus inventory supports sustainable practices by reducing waste, and creates room for newer product lines, thereby optimizing overall inventory management.
Table of Contents
Successful Surplus Trading of SILICON DIOXIDE in Solvents
A prominent chemical distributor recently turned their surplus of SILICON DIOXIDE into a strategic asset by listing it on a specialized trading platform. Faced with overproduction and limited storage capacity, they chose to sell excess inventory rather than waste valuable resources. The trade not only helped recoup unused capital and clear storage space, but it also provided buyers with a competitive edge by supplying high-quality SILICON DIOXIDE at a favorable price. This transaction set a precedent for efficient surplus management, reinforcing sustainability practices and optimizing operational costs across the solvents sector.