Maximizing Surplus Value: Discover CYANO PHENOL in the Solvents Sector
CYANO PHENOL is a versatile chemical compound, widely recognized for its unique properties and extensive applicability in industrial processes. As a solid chemical with high purity and specific technical attributes, CYANO PHENOL has become a vital component in solvent applications. When held as surplus inventory, it represents not only a valuable resource that can be reclaimed financially but also an opportunity to reduce waste and enhance operational efficiency. Its robust chemical profile makes it ideal for formulations that require precise performance, and its availability in surplus allows companies to manage storage effectively while freeing up critical warehouse space.
CYANO PHENOL Surplus Trading in Solvents – Optimizing Chemical Inventory Value
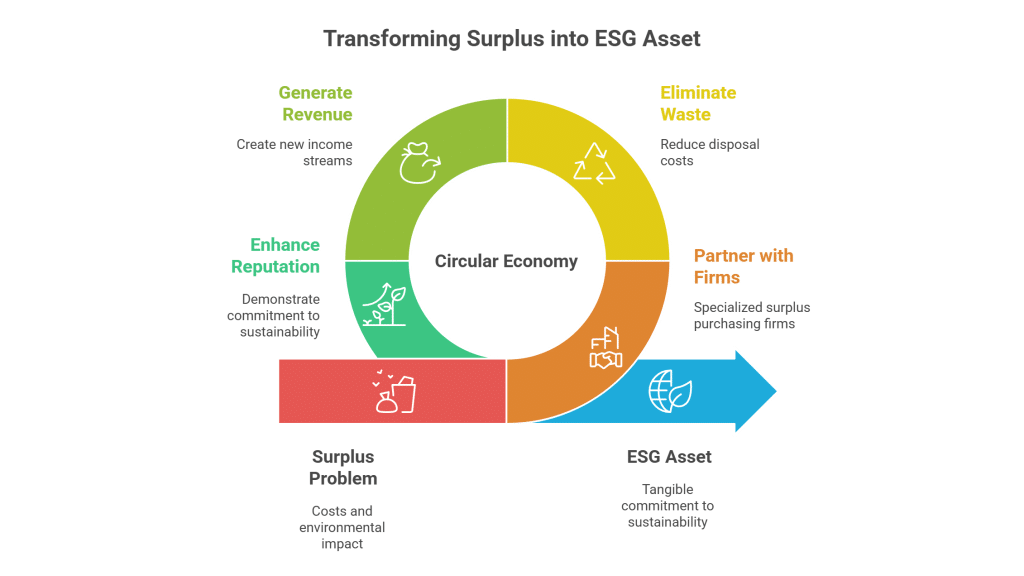
The practice of buying and selling surplus chemicals like CYANO PHENOL offers numerous benefits for both sellers and buyers. Manufacturers and distributors can recuperate costs from unused inventories, while procurement managers enjoy the advantage of sourcing high-quality chemicals at reduced prices. Additionally, the surplus trading process promotes sustainability by reducing waste and lowering disposal expenses. This efficient exchange process not only maximizes financial returns and operational flexibility but also contributes to safer environmental practices by ensuring that excess chemicals are repurposed rather than discarded.
Industrial Applications of CYANO PHENOL in the Solvents Sector
Buyers in the solvents sector benefit from accessing high-grade CYANO PHENOL at competitive prices, which aids in reducing production costs and improving profit margins. With surplus trading, procurement managers can integrate high-quality chemicals into their processes without the premium pricing typically associated with new batches. This not only secures a reliable source of essential compounds but also supports efforts to bolster sustainability and reduce environmental impact by reusing excess inventory.
For sellers, offloading surplus CYANO PHENOL means generating immediate revenue, freeing up storage space, and reducing the complexities of chemical disposal. It converts potential liabilities into economic gains by transforming excess stock into a valuable asset. Additionally, this practice reinforces an organization’s commitment to environmental stewardship by reintroducing a product into the market rather than resorting to costly and potentially hazardous disposal processes.
Table of Contents
Real-World Success: Transforming Surplus CYANO PHENOL into Strategic Advantage
A leading chemical manufacturer faced an excess inventory of CYANO PHENOL that was occupying valuable warehouse space and incurring storage costs. By participating in a structured surplus trading program, the organization was able to offload its surplus at competitive prices while a mid-tier solvent producer acquired a steady supply at reduced costs. This strategic maneuver not only alleviated storage issues but also enabled both parties to boost operational efficiency. The manufacturer recovered a significant portion of its production costs, and the buyer enhanced its formulation processes, leading to improved product quality and reduced environmental impact. The success story highlights how effective surplus chemical trading can mend financial, logistical, and environmental challenges simultaneously.