Elevate Your Cosmetic & Nutraceutical Formulations with Surplus Collagen Peptides
Collagen Peptides, a versatile protein derivative renowned for its hydrolyzed form, is revolutionizing the cosmetics and nutraceutical industries. As a surplus inventory item, these peptides offer exceptional value due to their high solubility, ease of incorporation, and consistent performance in anti-aging creams, serums, supplements, and other formulations. Companies holding excess stocks can now turn potential wastage into an asset, ensuring that high-quality ingredients do not go to waste.
Collagen Peptides in Cosmetics & Nutraceuticals - Unlock Surplus Value
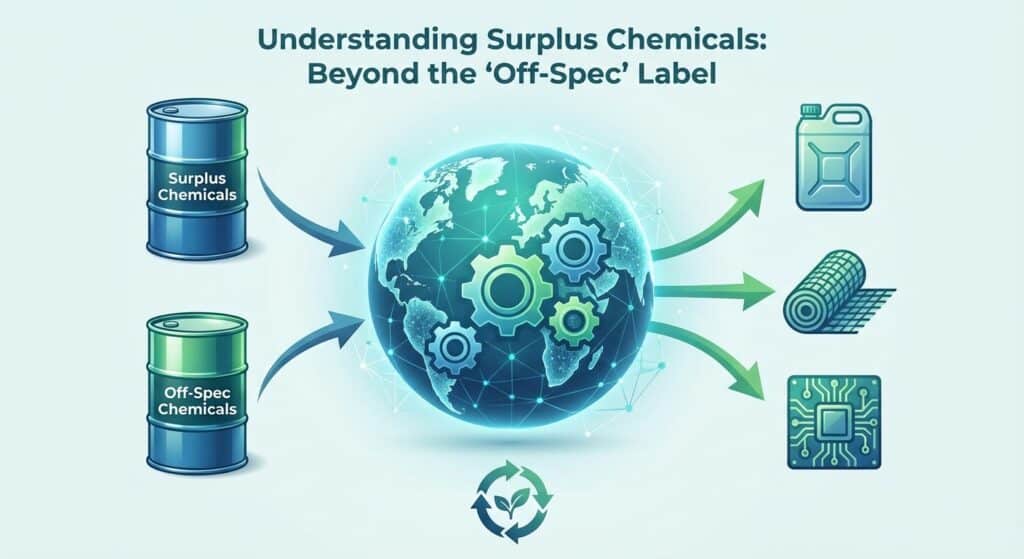
The dynamic market for surplus chemicals presents an opportunity for both offloading waste material and accessing cost-effective ingredients. Buying and selling surplus Collagen Peptides not only drives economic benefits such as cost recovery and freeing up valuable storage space but also promotes sustainability by reducing disposal-related expenses and mitigating environmental impacts. This innovative approach enables sellers to convert excess inventory into revenue while providing buyers with an affordable, reliable source of high-quality ingredients that meet strict regulatory standards and foster green practices.
Collagen Peptides in Cosmetics & Nutraceuticals Applications
Buyers benefit from accessing premium surplus Collagen Peptides at competitive prices, ensuring formulation efficiency without compromising on quality. The consistent quality and versatility of the peptides enable manufacturers to innovate and scale production while bolstering product credibility with ingredients that are recognized for safety, effectiveness, and strong environmental credentials.
Sellers stand to gain significant economic advantages by liquidating surplus or expired Collagen Peptides, turning potential waste into revenue. By clearing stock, companies reduce storage expenses, avoid costly waste disposal fees and regulatory complications, and contribute to sustainable practices by ensuring surplus chemicals are repurposed rather than discarded.
Table of Contents
Success Story: Converting Surplus Collagen Peptides into Sustainable Innovation
A leading cosmetic manufacturer recently transformed its surplus inventory of Collagen Peptides into a major asset. Struggling with excess material and increasing storage costs, the company decided to sell its unused stock on a surplus trading platform. Not only did they recoup significant costs by recovering storage expenses, but they also enabled a small startup to incorporate high-quality peptides into an innovative anti-aging serum. This win-win approach not only reduced potential disposal issues and regulatory penalties but also fostered stronger industry relationships built on sustainable practices and responsible resource management.