Harnessing the Potential of Surplus Cellulase in Textile and Biofuel Production
Cellulase is a vital industrial enzyme extensively used for fabric softening in the textile industry and for breaking down cellulose into fermentable sugars in biofuel production. Often arriving as surplus inventory due to overproduction or process adjustments, this enzyme presents an exciting opportunity for companies to repurpose excess stock. Its versatility makes it an essential chemical in industries driving innovation and efficiency in sustainable production processes.
Cellulase in Textile & Biofuel Production: Surplus Chemical Trading Solutions
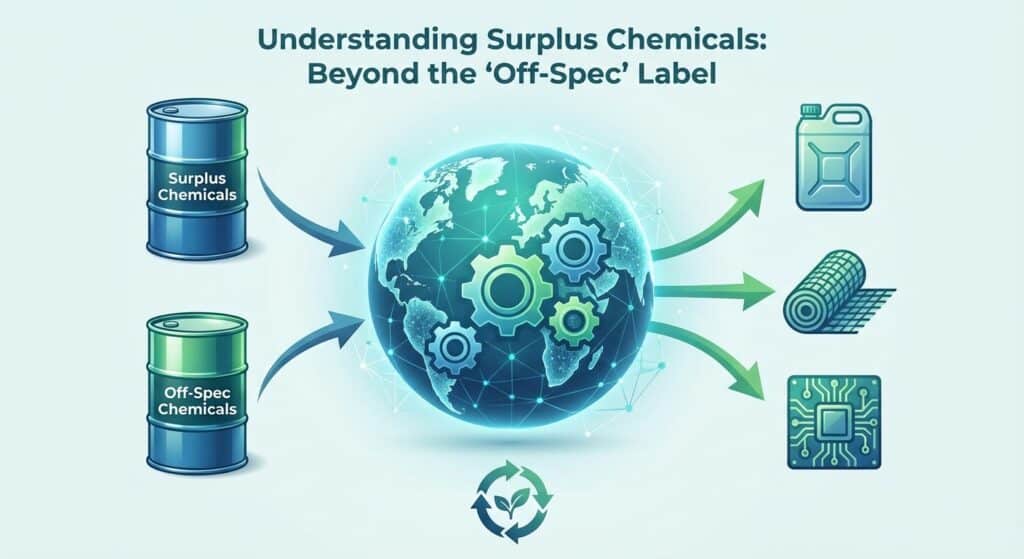
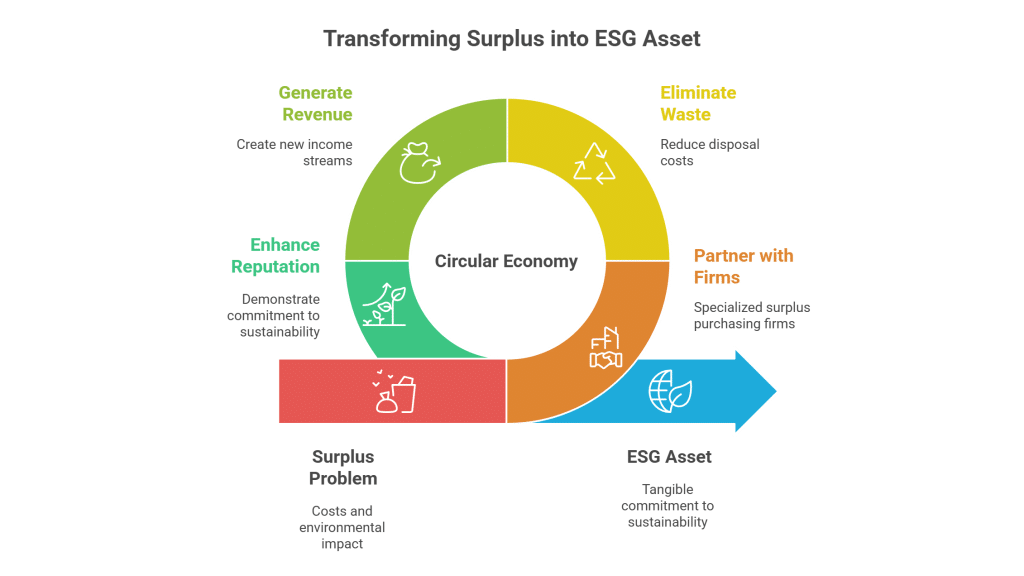
Engaging in the buying and selling of surplus cellulase offers significant economic and environmental benefits. Sellers can recover costs, free up valuable storage space, and avoid expensive disposal fees and stringent regulations. At the same time, buyers gain access to cost-effective, high-quality enzymes, ensuring reliable sourcing for their production needs. This mutually beneficial process supports sustainability by reducing waste and encouraging a circular economy, transforming a potential liability into a profitable asset.
Cellulase in Textile & Biofuel Production Applications
For buyers, surplus cellulase offers considerable cost savings along with the assurance of consistent quality. By sourcing surplus inventory, production processes remain uninterrupted while also contributing to an eco-friendly approach that reduces reliance on newly manufactured chemicals.
For sellers, liquidating surplus cellulase transforms excess stock into a revenue stream. It helps in reducing storage overheads, eliminates disposal costs, and supports environmentally responsible practices by ensuring the enzyme is used in productive applications rather than wasted.
Table of Contents
Successful Surplus Trading of Cellulase Transforming Production Efficiency
In one remarkable instance, a major textile manufacturer found itself with a significant surplus of cellulase due to process overproduction. Instead of incurring high disposal fees, the company decided to sell the excess enzyme through a strategic surplus trading platform. This decision not only alleviated storage constraints but also generated additional revenue that could be reinvested in further technology and process improvements. Meanwhile, a biofuel production plant sourced the surplus enzyme to enhance its biomass saccharification process, resulting in elevated sugar yields and improved overall efficiency. The successful transactions underscored the value of proactive surplus management, benefiting both sellers and buyers while promoting sustainable industrial practices.