Boron Carbide: Pioneering Surplus Strategies in Defense & Nuclear Energy
Boron Carbide is a high-performance advanced ceramic known for its exceptional hardness, lightweight properties, and durability. Commonly deployed in high-stress environments such as armor plating in defense applications and neutron shielding in nuclear reactors, this material often becomes surplus inventory when production exceeds immediate demand or project specifications evolve. Its robust characteristics make it indispensable in settings where both resilience and precision are required.
Boron Carbide: Advanced Ceramic Solutions in Defense & Nuclear Energy
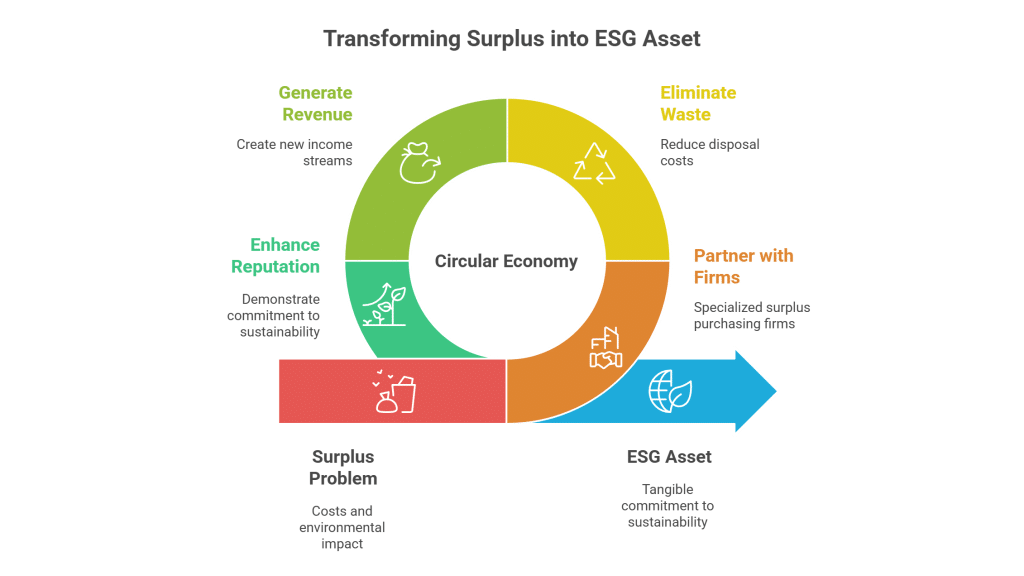
The trading of surplus chemicals like Boron Carbide offers significant advantages for both buyers and sellers. Companies can recover costs by selling excess inventory, free up valuable storage space, and avoid the financial burden of expensive disposal fees. Additionally, this approach supports sustainable practices by reducing waste and aligning with environmental regulations. In many cases, organizations not only save on disposal expenses but actually generate revenue by leveraging surplus materials, turning what might be considered a liability into a profitable asset.
Boron Carbide in Defense & Nuclear Energy
Buyers benefit from accessing premium, surplus-grade Boron Carbide at competitive prices. This cost-effective procurement reduces expenditure while providing a consistent supply of high-grade material for critical applications. Moreover, acquiring surplus stocks supports sustainable supply chain management by minimizing waste and reducing the environmental footprint associated with manufacturing new materials.
For sellers, offloading surplus Boron Carbide transforms storage challenges into financial benefits. By selling excess stock, companies can recover costs, free up warehouse space, and reduce the liabilities of long-term storage. Additionally, engaging in surplus trade mitigates the risks of non-compliance with environmental regulations and avoids the high costs associated with safe disposal.
Table of Contents
Revolutionizing Surplus Management in High-Stakes Industries
A prominent defense contractor recently encountered an overabundance of Boron Carbide when a change in project requirements led to surplus inventory. Instead of incurring high disposal fees, the company partnered with a surplus trading platform to convert the excess material into capital. This surplus was subsequently acquired by a nuclear facility to enhance the neutron shielding in its reactor systems. The successful trade not only streamlined inventory management but also underscored the sustainability of repurposing surplus advanced ceramics, thereby bolstering both defense and nuclear safety standards.